NYDFS Cybersecurity Rules Take Effect While Microsoft Expands AI Hiring: November 1, 2025 Security Update

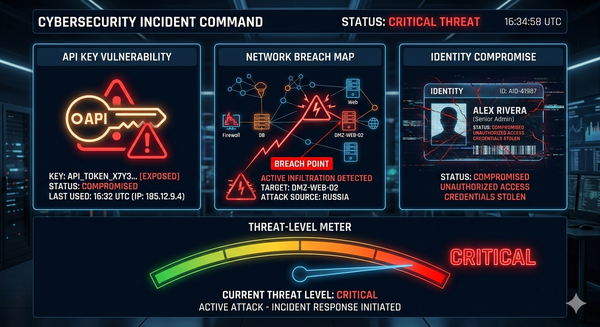
As I write this from home on November 1, 2025, the final phase of New York's stringent financial services cybersecurity regulations went into effect today. Simultaneously, we're dealing with a sophisticated Chinese state-sponsored attack exploiting a Windows zero-day to target European diplomats.
Regulatory deadlines and active nation-state campaigns don't usually coincide this perfectly. Today feels like a case study in why proactive cybersecurity compliance isn't optional anymore—it's survival.
NYDFS Part 500: The MFA Mandate Goes Full Force
The regulatory reality: As of today, November 1, 2025, the final cybersecurity requirements under New York's amended Part 500 regulation are now in effect. This means all covered financial entities must now implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for any user to access any information system.
Why this matters beyond New York:
I can tell you this isn't just a New York problem—it's a preview of what's coming nationwide. NYDFS has been clear that MFA deficiencies are the most exploited gap in cybersecurity breaches, making this one of their top enforcement priorities.
What I've been implementing for my financial services clients:
- Universal MFA: Not just for privileged accounts anymore—every user, every system, every time
- Written asset inventory procedures: Formal documentation for creating and maintaining information system inventories
- Compliance documentation: Detailed records that will be required for the April 15, 2026, annual certification
The regulation provides limited exemptions only for small businesses with specific revenue/asset thresholds, but the requirements are comprehensive and non-negotiable for everyone else.
Active Windows Zero-Day Targeting European Diplomats
The immediate threat: A China-linked hacking group (UNC6384) exploits an unpatched Windows shortcut vulnerability to target European diplomatic and government entities. Between September and October 2025, the attacks hit organizations in Hungary, Belgium, Italy, the Netherlands, and Serbia.
The attack methodology that has me concerned:
This isn't just another phishing campaign—it's a sophisticated multi-stage operation using spear-phishing emails themed around European Commission meetings and NATO workshops. The attackers are exploiting ZDI-CAN-25373 to deploy PlugX malware through DLL side-loading.
What makes this particularly dangerous:
- Zero-day exploitation: This is an unpatched vulnerability, meaning standard patching won't protect you
- Targeted themes: The emails use legitimate-looking diplomatic content that even security-aware users might trust
- Multi-stage deployment: The attack chain is designed to evade detection through multiple stages
My immediate recommendations for organizations:
- Enhanced email filtering: Implement additional scrutiny for diplomatic/government-themed emails
- URL analysis: Deploy advanced URL inspection for embedded links in emails
- Network segmentation: Isolate critical systems from potential compromise vectors
- Incident response readiness: Assume compromise and prepare response procedures
Nvidia and Samsung Announce Korean AI Megafactory
The strategic development: Nvidia and Samsung Electronics announced plans to construct an AI "megafactory" in South Korea, powered by over 50,000 of Nvidia's high-performance GPUs. This represents Nvidia's significant expansion into Asia's manufacturing heartland.
Why this matters for enterprise AI planning:
As someone who's been advising clients on AI infrastructure investments, this development signals several significant trends:
- Supply chain diversification: Reduced reliance on Taiwan-based production
- Asian AI hub development: Korea positioning itself as a major AI manufacturing center
- Scale economics: 50,000 GPUs in a single facility show the massive scale of modern AI infrastructure
The enterprise implications I'm discussing with clients:
This megafactory announcement validates the long-term AI infrastructure investment thesis while creating new procurement opportunities for organizations planning large-scale AI deployments.
Microsoft's AI-Driven Hiring Strategy
The workforce evolution: Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella announced plans to hire more employees but "with a lot more leverage" thanks to AI capabilities. This represents a fundamental shift in how technology companies think about human capital and AI augmentation.
What this signals for enterprise workforce planning:
Rather than replacing workers, Microsoft is betting on AI amplifying human capabilities. For my consulting clients, this provides a roadmap for thinking about AI integration—not as job replacement, but as capability enhancement.
The strategic takeaway: Organizations that successfully integrate AI to amplify human capabilities rather than replace them may achieve better long-term competitive advantages.
Critical Infrastructure Under Active Attack
Ribbon Communications Breach
The supply chain concern: Ribbon Communications, a provider of telecommunications services to the U.S. government and major telecom companies, revealed that nation-state hackers breached its IT network as early as December 2024.
Why this keeps me awake at night: Telecommunications infrastructure providers are high-value targets because they can provide access to multiple downstream customers. A single breach at this level can have cascading effects across the entire telecommunications ecosystem.
WSUS Vulnerability Being Actively Exploited
The Windows Server threat: A critical remote code execution vulnerability in Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), tracked as CVE-2025-59287, is actively exploited to deploy the Skuld infostealer.
I don't lose sight of the irony: Attackers are compromising the very systems designed to keep Windows environments secure. This highlights why I always recommend defense-in-depth strategies rather than relying on any single security mechanism.
FCC Plans to Eliminate Telecom Cybersecurity Requirements
The regulatory reversal: The Federal Communications Commission will vote next month on eliminating cybersecurity requirements for telecom carriers enacted following Chinese government cyberattacks on telecommunications infrastructure.
My professional concern:
FCC Chair Brendan Carr plans to undo the commission's declaration that telecommunications carriers must "secure their networks from unlawful access or interception of communications." Given the active nation-state campaigns we're seeing, this comes at precisely the wrong time.
The timing couldn't be worse: Just as we're dealing with sophisticated attacks on telecommunications infrastructure, reducing regulatory oversight seems counterproductive to national security objectives.
November 2025 Action Items for IT Directors
Immediate Compliance Actions (This Week)
- NYDFS Part 500: Verify MFA implementation across all systems for covered entities
- Windows Zero-Day: Implement enhanced email filtering for diplomatic/government-themed content
- WSUS Security: Review and harden Windows Server Update Services configurations
Long-term Initiatives (Q1 2026)
- Workforce AI Integration: Develop a strategy for AI-augmented human capabilities
- Supply Chain Security: Review telecommunications vendor security requirements
- Zero Trust Architecture: Implement defense-in-depth strategies beyond single security controls
My November 1st Assessment
November 1, 2025, perfectly captures the current cybersecurity reality—regulatory requirements are tightening just as sophisticated threats are intensifying. The convergence of NYDFS compliance deadlines with active nation-state campaigns demonstrates why reactive security is no longer viable.
Three critical insights from today:
- Compliance is becoming table stakes: NYDFS Part 500 represents the new baseline, not the gold standard.
- Nation-state threats target specific sectors: The diplomatic targeting shows how attackers are becoming more precise and strategic.
- AI infrastructure investment requires long-term thinking: The Nvidia-Samsung megafactory shows this isn't a short-term trend.
The strategic imperative: Organizations that view today's regulatory requirements as burdensome compliance costs rather than foundational security investments will find themselves increasingly vulnerable to the sophisticated threats we're seeing.
The fact that we're dealing with unpatched zero-days while major corporations announce AI hiring strategies and regulators implement stringent MFA requirements shows how complex the modern threat landscape has become. Success requires balancing immediate tactical responses with long-term strategic investments.
Reference Sources:
1. Hogan Lovells Legal Analysis - NYDFS Compliance Authority
- Comprehensive coverage of Part 500 final requirements and implementation details
- NYDFS Part 500 Requirements
2. The Hacker News - Critical Security Threats
- China-linked Windows zero-day attacks and VMware vulnerability exploitation
- The Hacker News
3. Cyware - Threat Intelligence and Breach Analysis
- Comprehensive coverage of active threats, including the Ribbon Communications breach
- Cyware Cybersecurity News
4. Federal News Network - Government Cybersecurity Policy
- Trump administration cybersecurity strategy development and federal agency guidance
- Federal News Network
5. Future Tech Blog - Technology Industry Analysis
- NVIDIA-Samsung AI megafactory announcement and Microsoft hiring strategy
- Future Tech Coverage