This Week in Cybersecurity: React Zero-Day, China's BRICKSTORM Campaign, and Critical Infrastructure Under Siege

December 3-5, 2025 | Weekly Threat Intelligence Briefing
This week brought a cascade of high-severity vulnerabilities and coordinated nation-state attacks, underscoring the increasingly hostile threat landscape facing IT leaders. From a critical remote code execution flaw in React Server Components that triggered emergency patching across millions of websites, to a joint CISA/NSA advisory exposing China's sophisticated BRICKSTORM malware campaign targeting VMware infrastructure, December 3-5 demonstrated that threat actors are operating at unprecedented speed and sophistication.
Here's what IT Directors and CISOs need to know from this week's developments.
1. CVE-2025-55182: The React Vulnerability That Broke the Internet
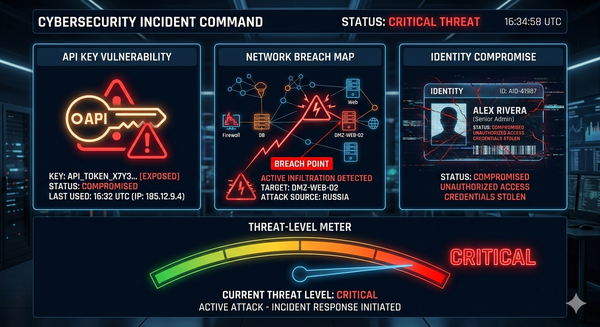
On December 3, 2025, the React team disclosed CVE-2025-55182, a maximum-severity (CVSS 10.0) remote code execution vulnerability affecting React Server Components. Within hours of public disclosure, Amazon Web Services threat intelligence teams observed active exploitation attempts by multiple China-nexus threat actors, including groups tracked as Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda.
What Happened
The vulnerability stems from unsafe deserialization in React's Flight protocol. Attackers can send specially crafted HTTP requests to vulnerable servers and achieve unauthenticated remote code execution. Security researchers at Wiz confirmed near-100% exploitation reliability in their proof-of-concept testing.
Critical Details
• Affected Versions: React 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0 and related react-server-dom packages
• Frameworks Impacted: Next.js, React Router (RSC mode), Waku, Vite RSC plugin, Parcel RSC plugin, RedwoodSDK
• Exploitation Timeline: China-nexus actors began exploitation attempts within hours of disclosure on December 3
• Scale: Approximately 39% of cloud infrastructures contain vulnerable versions (per Wiz)
• Default Vulnerable: Standard Next.js apps created with create-next-app are exploitable with no code changes
Immediate Actions
- Patch immediately: Update to React 19.0.1, 19.1.2, or 19.2.1
- Update Next.js: Deploy patched versions 15.0.5, 15.1.9, 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7, or 16.0.7+
- Enable WAF rules: AWS, Cloudflare, Google Cloud, and Akamai have all deployed detection rules
- Audit logs: Search for anomalous POST requests targeting RSC endpoints since December 3
2. CISA/NSA Alert: China's BRICKSTORM Malware Targeting VMware Infrastructure
On December 4, 2025, CISA, NSA, and the Canadian Cyber Centre issued a joint advisory warning of ongoing intrusions by Chinese state-sponsored actors using BRICKSTORM malware. The campaign targets VMware vCenter servers at government agencies and IT-sector organizations specifically.
The Threat Actor: WARP PANDA
CrowdStrike simultaneously published research on WARP PANDA, a newly identified China-nexus adversary responsible for the BRICKSTORM campaign. This threat actor has been operating since at least 2022 and demonstrates exceptional technical sophistication with deep knowledge of cloud and virtualization environments.
Campaign Details
• Targets: U.S.-based legal, technology, and manufacturing organizations
• Initial Access: Exploiting vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure, F5 BIG-IP, and VMware vCenter
• Persistence: Long-term access maintained from April 2024 through September 2025 in confirmed cases
• Malware Suite: BRICKSTORM, Junction, and GuestConduit (Go-based implants)
• Evasion: DNS-over-HTTPS, nested TLS channels, abuse of Cloudflare Workers and Heroku for C2
• Cloud Expansion: Pivoting to Microsoft Azure environments to access M365 data
Why This Matters
BRICKSTORM incorporates self-healing capabilities that automatically reinstall the malware if disrupted. The threat actors create hidden, unregistered VMs within vCenter environments and steal VM snapshots to extract credentials. Google Threat Intelligence estimates "dozens" of U.S. organizations have been compromised, with downstream victims from a SaaS provider being targeted.
Immediate Actions
- Run CISA's YARA/Sigma rules: Scan vCenter and ESXi environments for BRICKSTORM indicators
- Inventory edge devices: Audit all internet-facing Ivanti, F5, and VMware appliances
- Block unauthorized DoH: Restrict DNS-over-HTTPS to approved providers only
- Monitor vCenter privileged accounts: Watch for abuse of vpxuser and unusual VM operations
- Segment DMZ traffic: Block RDP/SMB from DMZ to internal networks
3. Cloudflare Outage: React Mitigation Cascades Into Global Disruption
On December 5, 2025, Cloudflare experienced its second major outage in three weeks when a WAF rule change deployed to mitigate CVE-2025-55182 triggered widespread service failures. The 25-minute incident affected approximately 28% of all HTTP traffic served by Cloudflare, taking down sites including LinkedIn, Zoom, Shopify, Fortnite, and numerous banking websites.
What Happened
While rolling out increased buffer sizes to protect customers from the React vulnerability, Cloudflare made a secondary configuration change to disable an internal WAF testing tool. This change propagated globally within seconds and caused error states in their FL1 proxy version under certain conditions, resulting in 500 Internal Server Errors across millions of customer sites.
Key Lessons
- CDN concentration risk is real: Organizations increasingly depend on a handful of infrastructure providers
- Rapid patching creates new risks: Emergency mitigations can introduce instability
- Multi-CDN strategies matter: Consider redundant CDN configurations for critical applications
4. CVE-2025-66516: Maximum-Severity XXE in Apache Tika
On December 4, 2025, Apache disclosed CVE-2025-66516, a critical (CVSS 10.0) XML External Entity injection vulnerability in Apache Tika. The flaw allows attackers to craft malicious PDF files containing embedded XFA data that, when processed, can read sensitive server files or enable server-side request forgery attacks.
Impact Assessment
Apache Tika is widely embedded in document processing pipelines, search indexing systems (Apache Solr and Elasticsearch), content analysis platforms, and compliance tools across the finance, legal, government, and media sectors. Any application that accepts PDF uploads from untrusted sources is potentially vulnerable.
Affected Versions
• Apache Tika core: 1.13 through 3.2.1
• Apache Tika parsers: 1.13 before 2.0.0
• Apache Tika PDF parser module: 2.0.0 through 3.2.1
Immediate Actions
- Upgrade tika-core to 3.2.2: The fix is in tika-core, not just the PDF module
- Audit document processing: Identify all applications using Tika for PDF parsing
- Disable PDF parsing temporarily: If immediate patching isn't feasible, disable Tika's PDF parsing capability
5. Record 29.7 Tbps DDoS Attack: Aisuru Botnet Demonstrates Unprecedented Scale
Cloudflare's Q3 2025 DDoS Threat Report, released December 3, revealed that the Aisuru botnet launched a record-breaking 29.7 terabits per second attack—the largest ever recorded. The botnet, comprising an estimated 1-4 million infected devices globally, is now available as a botnet-for-hire service for as little as $300.
Key Statistics
• Attack Peak: 29.7 Tbps (UDP carpet-bombing across 15,000 destination ports/second)
• Total Q3 Attacks: 8.3 million DDoS attacks blocked (40% increase YoY)
• Hyper-Volumetric Surge: 54% increase QoQ in attacks exceeding 1 Tbps
• AI Sector Targeting: 347% spike in DDoS traffic against AI companies in September
• Attack Duration: 71% of HTTP attacks and 89% of network-layer attacks lasted under 10 minutes
Critical Insight: Attacks are now too fast for human response or on-demand mitigation services. Organizations must implement always-on, automated DDoS protection.
Key Takeaways for IT Professionals
- Patch velocity is critical: China-nexus actors are weaponizing vulnerabilities within hours of disclosure. The React CVE demonstrated that even rapid, coordinated disclosure can't keep pace with sophisticated threat actors.
- VMware environments are high-value targets: BRICKSTORM's focus on vCenter infrastructure reflects a strategic shift toward virtualization platforms that provide access to entire organizational ecosystems.
- Infrastructure concentration creates systemic risk: Two Cloudflare outages in three weeks affecting millions of sites demonstrate the fragility of centralized internet infrastructure.
- Document processing is an attack vector: The Apache Tika XXE vulnerability shows that any system that processes untrusted files—PDFs, documents, uploads—exposes itself to potential attacks.
- DDoS-for-hire has crossed a threshold: Multi-terabit attacks are now commodity services available to any adversary with modest resources.
Sources
• React Team Security Advisory: CVE-2025-55182 (December 3, 2025)
• AWS Security Blog: China-nexus threat groups exploit React2Shell (December 4, 2025)
• CISA/NSA/Cyber Centre Joint Advisory: BRICKSTORM Backdoor (December 4, 2025)
• CrowdStrike: Unveiling WARP PANDA (December 4, 2025)
• Cloudflare Blog: December 5, 2025 Outage Post-Incident Report
• Apache Tika Security Advisory: CVE-2025-66516 (December 4, 2025)
• Cloudflare Q3 2025 DDoS Threat Report (December 3, 2025)
• Wiz Blog: Critical RCE Vulnerabilities in React and Next.js (December 3, 2025)
• Google Cloud Security Blog: Responding to CVE-2025-55182 (December 3, 2025)
• The Hacker News, BleepingComputer, SecurityWeek, Dark Reading (December 3-5, 2025)